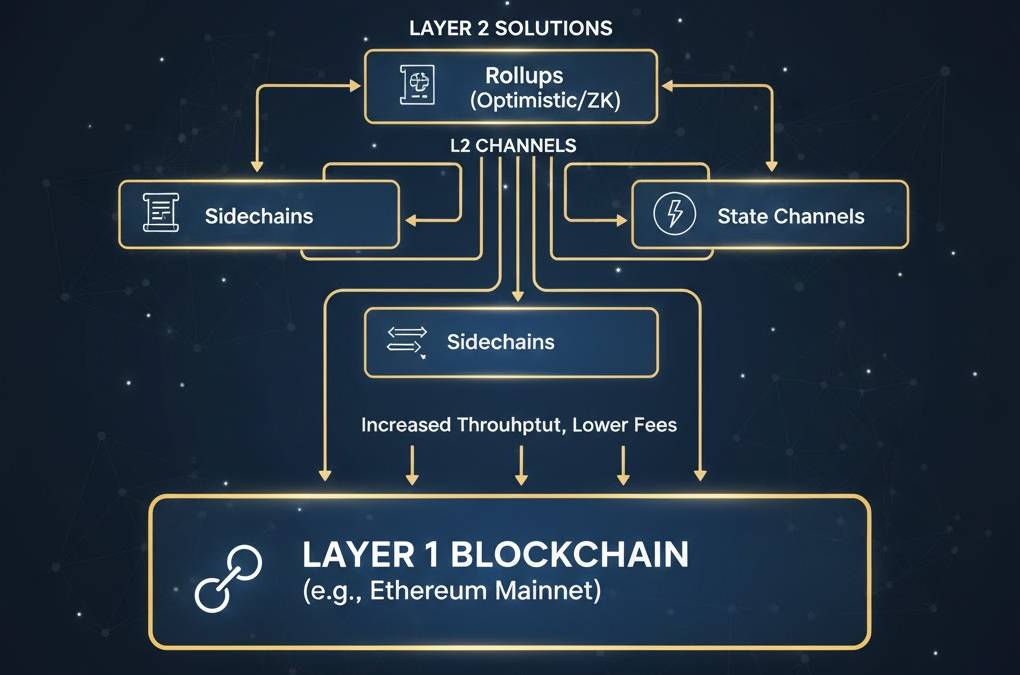
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Rollups, Channels & Sidechains
Understand Layer 2 solutions and how they solve blockchain scalability. Learn about Rollups, Plasma, and State Channels explained in detail.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Speed Without Sacrifice
Layer 2 solutions enable blockchains to process transactions faster and cheaper while maintaining security. Learn how Rollups, State Channels, and Plasma work and why they're crucial for blockchain adoption.